# Install Module
Install-Module -Name CybereasonAPI
# OR
Install-Module -Name CybereasonAPI -ForceVERSION: Tested with latest version of Cybereason API v20.2. Most of these should work with as low as version 18.0.
IMPORTANT NOTE ON TWO FACTOR AUTHENTICATION: Cybereason has two permission types that can communicate with the API. There is an API user, which needs to be created manually and a GUI User. A GUI user has the ability to sign into the Cybereason Web app and can perform queries against the main Cybereason API site. This site specifically is https://sage.cybereason.com/rest/* That same GUI user however is NOT able to perform queries that for affect isolation rules or other Malop related tasks. These queries get performed against your organizations Cybereason server which is something like this: https://abcdefgh.cybereason.com/rest/. (This URL value would be whatever value you enter into the -Server switch parameter in the Connect-CybereasonAPI cmdlet). Only the created API user, who does not have permissions to sign into the Cybereason Web GUI, is able to perform API actions dealing with Malops and Isolation rules.
CybereasonAPI is a PowerShell module containing commands meant to allow simple interaciton with the Cybereason API. To use the API there are some cmdlets that require you to authenticate with an API user and others you are able to use a full privileged S3 account. Cybereason has defined a total of 9 general categories of reference for their API.
- Hunt and Investigate (Still In Progress)
- Respond to Malops (Still In Progress)
- Remediate Items (Completed)
- Respond to Malware (Completed)
- Manage Reputations (Completed)
- Add Custom Detection Rules (Completed)
- Get Threat Intel (Completed)
- Manage Sensors (Still In Progress)
- Set Machine Isolation Rules (Completed)
RESOURCE: Cybereason API Documentation
I have come up with some cmdlets for the above categories to allow simplified communication from a Windows PowerShell window. Any contributions to this project are welcome as there is a ton of information to go through.
If you find an issue with any of the cmdlets in this module please let me know. There are a few cmdlets I have not tested out yet, the Isolation Rules inparticular and Respond To Malware I have not fully tested. If you want to send me an email with the PowerShell error message you received it will be very helpful. Thank you. [email protected]
Connect-CybereasonAPI:
This cmdlet is used to authenticate to the Cybereason API. This will create a global variable called $Session that will get used with the rest of the cmdlets in this module that need it.
# AUTHENTICATE AS THE API USER (Currently not able to enable TFA for API users)
Connect-CybereasonAPI -Username '[email protected]' -Passwd 'Password123!' -Server 'aaaaaaaa.cybereason.net' -Port '443'
# This authenticates to the Cybereason API creating a session that gets used with all cmdlets in this module
# AUTHENTICATE AS AN GUI USER WHO HAS TFA ENABLED
Connect-CybereasonAPI -Username '[email protected]' -Passwd 'OnlyPassword1!' -Server 'aaaaaaaa.cybereason.net' -Port '8443' -ClearHistory -Authenticator 123456
# This authenticates to the Cybereason API using Two Factor Authentication. This also clears the PowerShell command history in the current session and in the fileGet-CybereasonReputation:
This cmdlet is used to view or download a CSV list of reputation information that have been manually configured on your environments Cybereason server.
Documentation for Manage Reputations
- Return a list of reputations that have been configured on Cybereason for your environment and view it in CSV format in your terminal window
- Return a list of reputations that have been configured on Cybereason for your environment and view it in CSV format and save it to a file
Get-CybereasonReputation -Verbose
# OR TO SAVE TO CSV FILE
Get-CybereasonReputation -Path C:\Windows\Temp\CybereasonReputations.csvSet-CybereasonReputation:
This cmdlet is used to add or update a custom reputation on the Cybereason server instance. Using the Cybereason Reputation Management API, you can integrate and update threat intelligence from various sources to improve detections, view and update file reputations, and add items to the whitelist based on behavioral characteristics.
- Add or remove reputations for a file using its hash or filename by adding it to a whitelist or blacklist. You can also prevent execution of the file throughout your environment
- Add or remove reputations for an IP address by adding it to a whitelist or blacklist
- Add or remove reputations for a domain by adding it to a whitelist or blacklist
Set-CybereasonReputation -Keys '1.1.1.1' -Modify whitelist -Action Add -PreventExecution false -Verbose
Set-CybereasonReputation -Keys '8.8.8.8','www.cybereason.com' -Modify whitelist -Action Remove -PreventExecution false -Verbose
Set-CybereasonReputation -File 'C:\Users\Enemy\badFile.exe','C:\Users\Enemy\persistence.exe' -Modify blacklist -Action Add -PreventExecution true -VerboseThis cmdlet is used to communicate with every link under the "Get Threat Intel" section of the API documentation.
Get-CybereasonThreatIntel:
can perform the following actions.
- Get a file reputation
- Get reputation for a domain
- Get reputation for an IP address
- Retrieve product classification information
- Retrieve process classification information
- Retrieve process hierarchy information
- Retrieve file extension information
- Retrieve port information
- Retrieve collection information
- Retrieve a list of IP address reputations
- Retrieve a list of domain reputations
- Check for database updates
Documentation for Get Threat Intel
Get-CybereasonThreatIntel -Domain 'www.cybereason.com','cybereason.com'
Get-CybereasonThreatIntel -IPAddress '1.1.1.1','1.0.0.1'
Get-CybereasonThreatIntel -MD5Hash FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
Get-CybereasonThreatIntel -DbUpdateCheck -ReputationAPI product_classificationBy using the API you can retrieve details on malware. This enables you to address and investigate malware to prevent additional damage.
- Get a count of all Malware per type
- Query a specific type of Malware
Documentation for Respond to Malware
Get-CybereasonMalwareCount:
This cmdlet is used to return all of the Malware counts on Cybereason
# This example returns the count for all Malware types in Cybereason
Get-CybereasonMalwareCountGet-CybereasonMalwareType:
This cmdlet is used to query Malware from a start date, all malware, all malware that needs attention, or all malware with a status of done.
Get-CybereasonMalwareType -MalwareType KnownMalware -NeedsAttention -Limit 1 -Sort ASC
# This example returns 1 result on all malware that needs attention in ascending order of their occurences
Get-CybereasonMalwareType -MalwareType KnownMalware -All -Limit 25 -Sort DESC -Offset 0
# This example returns up to 25 results on all known malware in descending order
Get-CybereasonMalwareType -MalwareAfter (Get-Date).AddDays(-2).Ticks
# This example returns info on all known malware that occured after a defined date
Get-CybereasonMalwareType -MalwareBefore (Get-Date).AddDays(-2).Ticks
# This example returns info on all known malware that occured before a defined date
Get-CybereasonMalwareType -MalwareType KnownMalware -Status Done -Limit 25 -Sort DESC -Offset 0
# This example returns info on all known malware with a status of doneBy using the API you can take remediation actions on Malops to limit or prevent additional damage.
- Remediate an item
- Check the status of a remediation
- Abort a remediation operation
- Get remediation statuses for a particular Malop
Documentation for Remediate Items
Invoke-CybereasonRemediateItem:
This uses the Cybereason API to perform a remediation action on a specific file, process, or registry key.
Invoke-CybereasonRemediateItem -MalopID "11.2718161727221199870" -InitiatorUserName "[email protected]" -MachineID "-1632138521.1198775089551518743" -ActionType KILL_PROCESS
# This example remediates a process by killing it after it was discovered by a Malop
Invoke-CybereasonRemediateItem -InitiatorUserName "[email protected]" -MachineID "-1632138521.1198775089551518743" -TargetID "-2095200899.6557717220054083334" -ActionType KILL_PROCESS
# This example remediates a process that was not involved in a MalopGet-CybereasonRemediationProgress:
This cmdlet is used too return details on the progress of a specific remediation operation.
Get-CybereasonRemediationProgress -Username '[email protected]' -MalopID '11.2718161727221199870' -RemediationID '86f3faa1-bac0-4a17-9192-9d106b734664'
# This example gets the current status on a Malop that was remediated by the user [email protected]Stop-CybereasonMalopRemediation:
This cmdlet aborts a remediation operation on a specific Malop.
Stop-CybereasonMalopRemediation -MalopID '11.2718161727221199870' -RemediationID '86f3faa1-bac0-4a17-9192-9d106b734664'
# This example aborts the remediation action take on the defined MalopGet-CybereasonRemediationStatus:
This cmdlet retrieves details about remediation actions performed on a particular Malop.
Get-CybereasonRemediationStatus -MalopID '11.2718161727221199870'
# This example gets the current status for the defined MalopNormally, when a machine is isolated, there is absolutely no communication allowed with the machine. This can sometimes limit the ability of an analyst or administrator to perform investigation or triage on that machine. However, you can add isolation exception rules to help you allow limited communication to an isolated machine
- Get-CybereasonIsolationRule:
Retrieve a list of isolation rules
Get-CybereasonIsolationRule
# This example retrieves a list of all rules for isolating specific machines- New-CybereasonIsolationRule:
Create an isolation rule
New-CybereasonIsolationRule -IPAddressString '123.45.67.89' -PortNumber 8443 -Blocking -Direction ALL
# This example creates a new isolation rule that blocks All communication to 123.45.67.89- Set-CybereasonIsolationRule:
Update an isolation rule
Set-CybereasonIsolationRule -RuleID "5a7b2e95e4b082f2e909a4f3" -IPAddressString '123.45.67.89' -PortNumber 8443 -Blocking -Direction ALL
# This example creates a new isolation rule that blocks All communication to 123.45.67.89- Remove-CybereasonIsolationRule:
Delete an isolation rule
Remove-CybereasonIsolationRule -RuleID '5859b3d0ae8eeb920e9d2f4e' -IPAddressString '1.1.1.1' -PortNumber 8443 -Direction ALL -LastUpdated 1525594605852
# This example deletes the isolation rule that is blocking all traffic to 1.1.1.1
Remove-CybereasonIsolationRule -RuleID '5859b3d0ae8eeb920e9d2f4e' -IPAddressString '10.10.10.10' -PortNumber 8443 -Blocking -Direction OUTGOING -LastUpdated 1525594605852
# This example deletes the rule ID that has IP address 10.10.10.10 outbound traffic blockedDocumentation for Machine Isolation Rules
Custom detection rules created via API should be created only after adequate research regarding precision and coverage has been completed. Creating a custom detection rule that is not specific enough can have detrimental impact on retention and overall performance of the environment.
- Retrieve a list of all active custom detection rules
- Retrieve a list of all disabled custom detection rules
- Retrieve a list of all available root causes
- Retrieve a list of all available Malop detection types
- Retrieve a list of all available Malop activity types
- Create a custom rule
- Update a custom rule
- Get the modification history
Documentation for Add Custom Detection Rules
Get-CybereasonCustomDetectionRule -ActiveRules
# This eample returns a list of all custom rules currently active in your environment.
Get-CybereasonCustomDetectionRule -DisabledRules
# This eample returns a list of all custom rules currently disabled in your environment.
Get-CybereasonCustomDetectionRule -RootCauses
# This eample returns a list of all Elements you can use for a root cause for a Malop generated from this custom rule.
Get-CybereasonCustomDetectionRule -DetectionTypes
# This eample returns a list of all available detection types you can use for the custom detection rule.
Get-CybereasonCustomDetectionRule -ActivityTypes
# This eample returns a list of all available Malop activity types you can use for the custom detection rule.
Get-CybereasonCustomDetectionRule -RuleID 1582038865368 -ModificationHistory
# This eample returns details on modifications made to a custom rule.
New-CybereasonCustomDetectionRule
# Still finishing help and testing to make sure it works as expected
Set-CybereasonCustomDetectionRule
# Still finishing help and testing to make sure it works as expectedUsing hunting queries and file search capabilities in the API, further your investigation of malicious behavior in your organization, including:
- Run investigative queries
- Search for files
- Get results of a previous file search
- Get results of a previous file search and export to CSV
- Return previous file searches
- Return previous file searches for all users
- Download a file
- Abort a file download operation
All of these capabilities help you improve security, uncover bad practices and deficiencies, and gain insight on tactical and strategic methods for threat prevention in your environment
Documentation for Hunt and Investigate
By using the API you can retrieve Malops or isolate machines involved in a specific Malop. This can prove to be very useful in situations where you are remediating Malops in your ticketing system and you would like to synchronize that system with Cybereason Malop inbox.
- Get all Malops currently active
- Retrieve all Malops of all types
- Retrieve details on a specific Malop
- Perform all possible response actions on a Malop
- Perform all possible response actions on a Malop
- Isolate a machine connected with a Malop
- Remove a machine involved with a Malop from isolation
- Update a Malop’s status
- Add a comment to a Malop
- Get a list of Malop labels
- Create a Malop label
- Delete a Malop label
- Update Malop labels
Documentation for Respond to Malops
Cybereason enables you to manage your Sensors from the API, including configuring NGAV settings for the sensors, starting and stopping collection on the Sensors, restarting Sensors, deleting or removing Sensors, archiving Sensors, and upgrading Sensors. (Get-Sensor, Set-Sensor, Remove-Sensor, Restart-Sensor, Create-Sensor, Add-Sensor, Update-Sensor, Save-Sensor)
- Get a list of all Sensors
- Retrieve a list of all actions on Sensors
- Set the Anti-Ransomware mode for a Sensor
- Set the Application Control mode for a Sensor
- Set the Anti-Malware status for a Sensor
- Set the Powershell protection mode for a Sensor
- Start collection on a Sensor
- Stop collection on a Sensor
- Delete a Sensor
- Restart a Sensor
- Retrieve logs from a Sensor
- Download logs from a Sensor
- Download a CSV list of Sensors
- Upgrade the Sensor
- Abort in-progress operations
- Archive a Sensor
- Remove a Sensor from archive
- Add/update or remove Sensor tags
- Retrieve Sensor tags for a Sensor
- Retrieve a list of sensor group
- Create a sensor group
- Edit a sensor group
- Add a sensor to a sensor group
- Remove a sensor from a group
Documentation for Manage Sensors
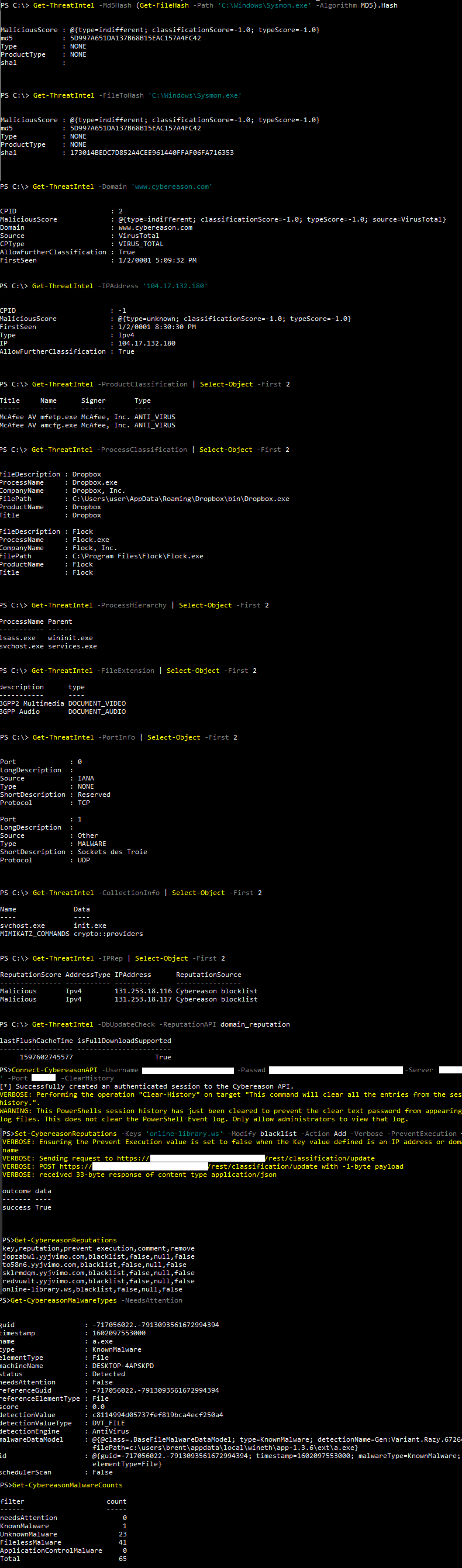
Below are images of the results from different Get-CybereasonThreatIntel commands.