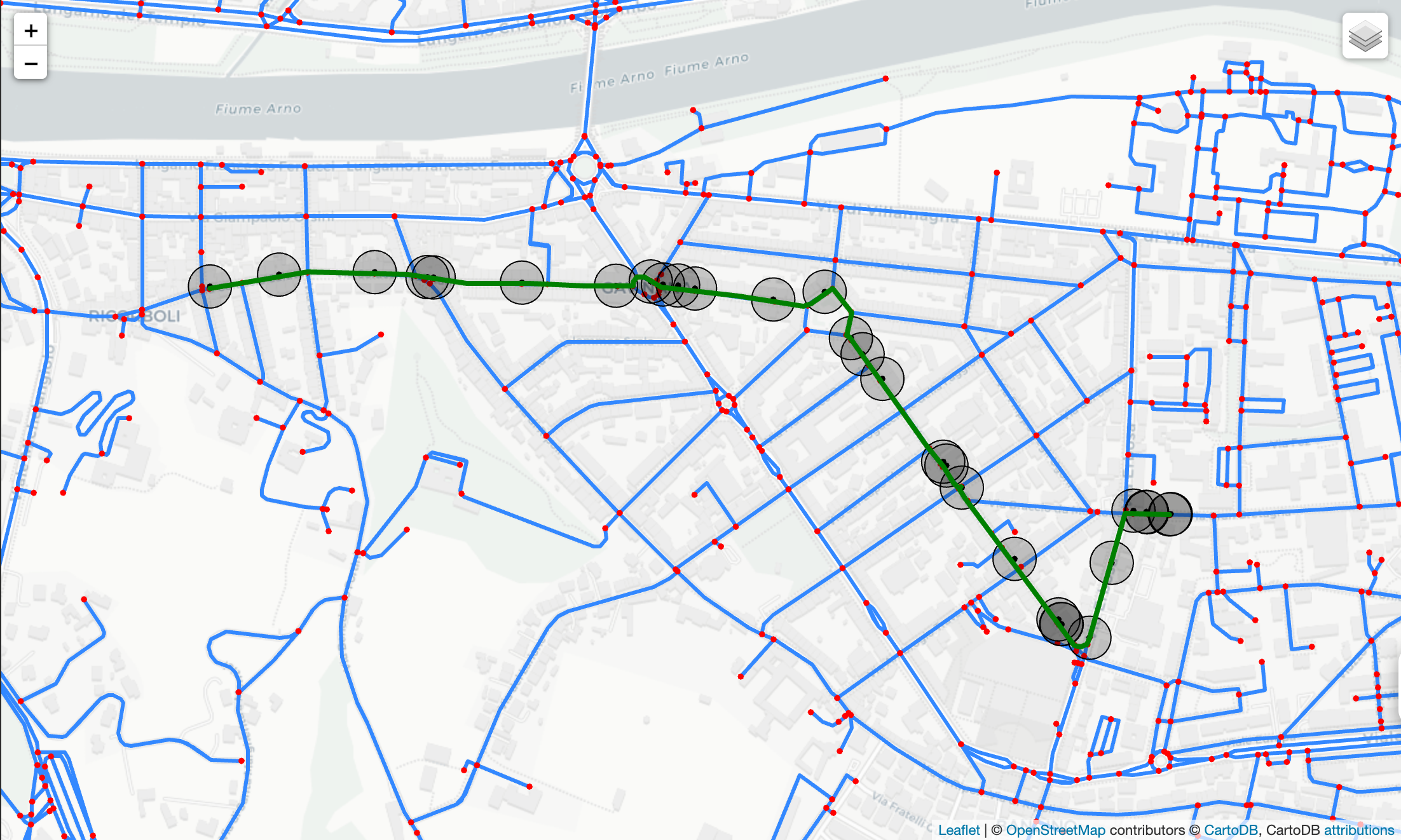
PyTrack is a Python package that integrates the recorded GPS coordinates with data provided by the open-source OpenStreetMap (OSM). PyTrack can serve the intelligent transport research, e.g. to reconstruct the video of a vehicle’s route by exploiting available data and without equipping it with camera sensors, to update the urban road network, and so on.
If you use PyTrack in your work, please cite the journal article.
Citation info: M. Tortora, E. Cordelli and P. Soda, "PyTrack: a Map-Matching-based Python Toolbox for Vehicle Trajectory Reconstruction," in IEEE Access, vol. 10, pp. 112713-112720, 2022, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3216565.
@ARTICLE{mtpytrack,
author={Tortora, Matteo and Cordelli, Ermanno and Soda, Paolo},
journal={IEEE Access},
title={PyTrack: A Map-Matching-Based Python Toolbox for Vehicle Trajectory Reconstruction},
year={2022},
volume={10},
number={},
pages={112713-112720},
doi={10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3216565}}The following are the main features that PyTrack includes:
- Generation of the street network graph using geospatial data from OpenStreetMap
- Map-matching
- Data cleaning
- Video reconstruction of the GPS route
- Visualisation and analysis capabilities
The source code is currently hosted on GitHub at: https://github.com/cosbidev/PyTrack. PyTrack can be installed using*:
# conda
conda install pytrack # or PyPI
pip install PyTrack-lib*for Mac m1 users, it is recommended to use conda in order to be able to install all dependencies.
Checkout the official documentation. Besides, here you can see some examples of the application of the library.
To see the map-matching feature of PyTrack in action please go to map-matching documentation.
All contributions, bug reports, bug fixes, documentation improvements, enhancements, and ideas are welcome.
Created by Matteo Tortora - feel free to contact me!
PyTrack is distributed under a BSD-3-Clause-Clear Licence.